The space industry has been expanding its market size due to the entry of private companies and technological innovations.
Beyond traditional government-led projects, the industry is now full of potential, encompassing rocket reuse technology, satellite miniaturization, and space tourism.
But within this rapidly growing space business sector, what steps should one take to build a career? What kinds of companies, job openings, and career transition options exist?
As of 2026, the industry is in the midst of an unprecedented “war for talent”.
This is largely driven by the “Space Strategy Fund” (1 trillion yen over 10 years), which has supplied hundreds of billions of yen to the private sector over the past two years. Consequently, many startups are shifting from the R&D phase to specific service provision and mass production phases, significantly increasing the need for not only engineers but also business roles such as BizDev (Business Development), finance, and legal to achieve profitability.
This article explains the current state and future outlook of the space industry, also known as Space Tech, based on the latest information.
It details major industry players, notable space startups, the latest technological trends, and the most recent job market trends observed daily by space industry-specialized recruitment consultants, including hiring trends beyond 2026.
It provides a practical guide for engineers, researchers, and business professionals aiming for a career in the space industry.
I hope this industry map serves as a valuable resource and a great first step toward achieving your career transition into the Japanese space industry.

Overview of the Space Business Industry
1. Market Growth
The global space industry market reached approximately 54 trillion yen in 2022 and is projected by Morgan Stanley to reach 140 trillion yen by 2040.
This growth speed is remarkable when compared to the automobile industry, which took over 100 years to reach a market size of about 400 trillion yen.
The industry is shifting from government-led to private-led, with commercial satellite services and space transportation now accounting for about three-quarters of the market. (Current market breakdown: Approximately one-fourth of the total is government budgets, and approximately three-fourths is commercial satellite services and space transportation-related services provided by private companies)
*Calculated at 140 yen per dollar
2. The Current State of Space Development in Japan
Historically, Japan’s space development was led by JAXA and major heavy industry/electronics manufacturers such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, SKY Perfect JSAT, NEC, and Toshiba.
Recently, there has been a surge of about 100 startups, including:
- ispace: Lunar exploration and transportation services.
- QPS Institute: Development of small SAR satellites for all-weather ground observation.
- Astroscale: On-orbit services, including space debris removal.
- Axelspace: Micro-satellite development and Earth observation services.
- Synspective: SAR satellite development and data solutions.
Japan’s current space market is approximately 4 trillion yen, but the government aims to double this to 8 trillion yen by the early 2030s.
To support this, the “Space Strategy Fund” provides up to 300 billion yen for 22 themes across transportation, satellites, and exploration.
3. Technological Trends
Key technological trends include reusable rockets, space debris removal, satellite miniaturization, and satellite constellations.
These technologies have significantly reduced the cost of access to space.
Furthermore, the 2024 “Space Technology Strategy” emphasizes lunar landing, communication, and resource development.
(Source: March 2024, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.‘The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s (METI’s) initiatives in light of trends in the space industry at home and abroad, and the future.’
Industry map of the space industry
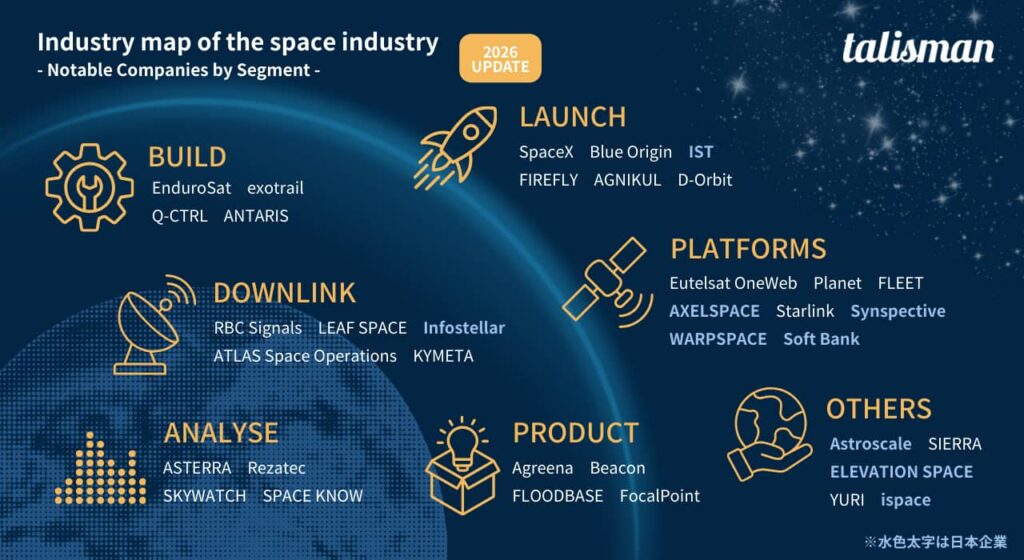
The space tech industry map summarises the companies of note by segment and the top countries in terms of the number of companies in the space tech domain.
Looking at the segments, it can be seen that Japanese companies (shown in light blue bold) are the focus of attention for their activities in the areas of ‘Platform’ and ‘Other (services, etc.)’.
In terms of the number of companies by country, the USA is in first place with almost 6,400 companies, far ahead of the second place and accounting for half of the world’s total number of companies. Japan ranks twelveth in the world with approximately 190 companies, and third in Asia after China and India.
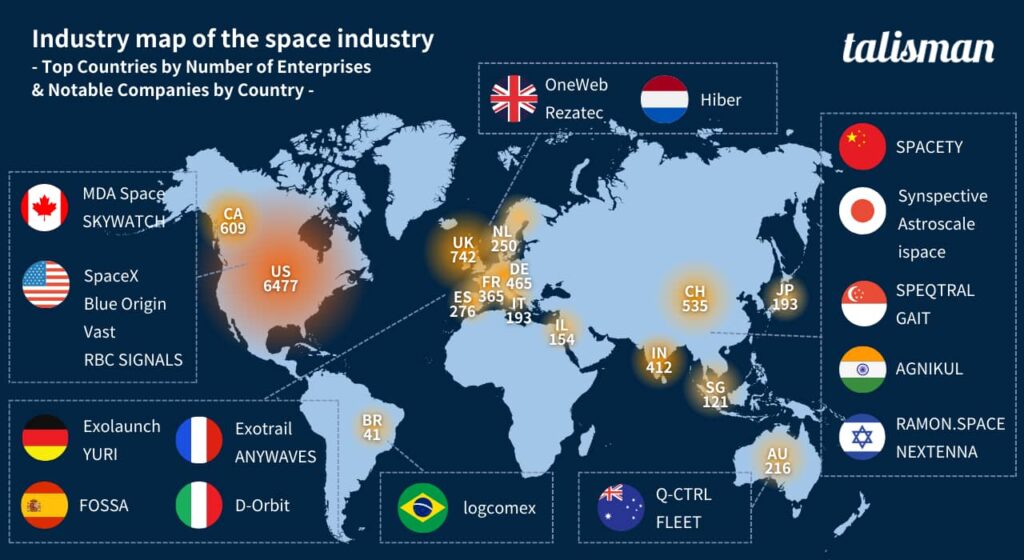
(The number of featured companies and companies by country was compiled by the TJ2 editorial team based on the following site. 「SpaceTechMap2024」「SpaceTech Industry 2021 Landscape Overview」)
The following is a list of companies listed in the SpaceTechMap 2024, published by Seraphim Space, the world’s largest investment company specialising in the space sector. You can also search by category, which is useful for gathering information.
The category ‘UPSTREAM’ in the table indicates business areas in infrastructure, such as the manufacture and launch of rockets and satellites. DOWNSTREAM’ refers to business areas that utilise data acquired mainly from space.
| 大分類 | 中分類 | 小分類 | 企業名 / Website | 国 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | Magdrive | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | ION-X | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | GENERAL GALACTIC | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | MORPHEUS SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | Benchmark Space Systems | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | Agile Space Industries | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | PHASEFOUR | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | Exotrail | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | ORBION | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE PROPULSION | Ursa Major | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | Orbitworks | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | AscendArc | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | ArkEdge Space | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | ENDUROSAT | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | aerospacelab | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | albaorbital | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | OPEN COSMOS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | LOFT ORBITAL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | nano avionics | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | YORK SPACE SYSTEMS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | BLUE CANYON TECHNOLOGIES | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | APEX | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | ASTRO DIGITAL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | REFLEX AEROSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | MDA | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | AAC CLYDE SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | MuonSpace | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | NEWORBIT | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | K2 SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | SATLANTIS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | TERRAN ORBITAL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | GOMSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SATELLITES | reorbit | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Tron Future Tech | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | mPower Technology | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Dcubed GmbH | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | CesiumAstro | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | SOLESTIAL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | HADRIAN | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | PSIONIC | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | CAMBIUM | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Swissto12 | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | AKASH SYSTEMS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | UBOTICA | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Carbice | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Q-CTRL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | Freeform | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | MACHINA LABS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | OXFORD SPACE SYSTEMS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SPACE HARD WARE SUBCOMPONENTS | RAMON.SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | PiLogic | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | Defense Unicorns | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | Kayhan.space | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | quindar | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | SEDARO | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | lean space | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | AALYRIA | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | COGNITIVE SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | ANTARIS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE IN-SPACE | KYTHERA SPACE SOLUTIONS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | Revel | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | Nominal | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | FIRST RESONANCE | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | SIFT | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | VIOLETLABS | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | Integrate | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | STELL | |
| UPSTREAM | BUILD | SOFTWARE TERRESTRIAL | Epsilon3 | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | STOKE Space Technologies | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | Latitude | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | GILMOUR SPACE TECHNOLOGIES | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | DAWN AEROSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | SPACE X | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | ROCKETLAB | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | X-BOW | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | SPIN LAUNCH | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | Isar Aerospace | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | SKYRORA | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | Relativity | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | FIREFLY | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | RFA | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | BLUE ORIGIN | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | INTERSTELLAR TECHNOLOGIES | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | AGNIKUL | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | PHANTOM SPACE CORPORATION | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | ASTRA | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | AURIGA | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | SKYROOT | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | LAUNCHERS | ORBEX | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | Portal Space Systems | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | ARGO SPACE CORP | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | EXO LAUNCH | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | D-Orbit | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | TRANSASTRA | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | MOMENTUS SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | IMPULSE SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | LAUNCH | SPACE TUGS | EPIC AEROSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | univity | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | Logos Space Services | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | LYNK | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | STARLINK | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | Xona Space Systems | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | Eutelsat OneWeb | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | AST | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | RIVADA | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | SPEQTRAL | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | WARPSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | TRUSTPOINT | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | E-SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | ASTRANIS | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | omnispace | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | Kacific | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | SKYKRAFT | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS CONNECTIVITY | MANGATA | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | FLEET | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | kineis | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | astrocast | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | FOSSA | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | SATELIOT | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | Myriota | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | hubble | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | OQ TECHNOLOGY | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS IOT | eSAT GLOBAL | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | SatVu | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Orora Tech | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Matter Intelligence | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | QPS研究所 | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | HawkEye360 | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | ARRAY LABS | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | AXELSPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Wyvern | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Hydrosat | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | constellr | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | pixxel | US/ |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | NUVIEW | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | spire | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | OSK | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | ALBEDO | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | ICEYE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | planet | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | PLANETiQ | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Capella Space | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | unseenlabs | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | Synspective | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | GHGSAT | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | BLACK SKY | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | tomorrow.io | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | UMBRA | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | SATELLOGIC | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | SATELLITE CONSTELLATIONS REMOTE SENSING | KUVA SPACE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | WindBorne Systems | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | Sorcerer | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | NewSpace | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | AALTO | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | urban sky | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | SKYDWELLER | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | SCEYE | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | NEAR SPACE LABS | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | KRAUS HAMDANI | |
| UPSTREAM | PLATFORMS | HAPS | WORLD VIEW | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | quvia | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | MBRYONICS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | ANYSIGNAL | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | QuadSAT | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | Kognitive Networks | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | Slyloom | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | Infostellar | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | mynaric | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | RBC SIGNALS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | TRANSCELESTIAL | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | CONNEKTICA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | ATLAS SPACE OPERATIONS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | LEAF SPACE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | skylo | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | BRIDGE COMM | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | cailabs | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | COMMUNICATIONS | ACCELERCOMM | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | Skynopy | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | Northwood Space | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | goTenna | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | Farcast | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | ALL. SPACE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | Greener wave | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | requtech | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | KYMETA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | sofant tachnologies | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | hiber | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | QUASAR SAT | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | NEXTENNA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | oneNav | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | GROUND TERMINALS | hiSky | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | Ocient | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | ID Quantique | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | HEQAsecurity | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | ThinkQuantum | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | KETS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | ARMADA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | SpiderOak | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | Crypta Labs | |
| DOWNSTREAM | DOWNLINK | SECURITY&STORAGE | REBEL SPACE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Space Intelligence | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | meteomatics | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | HABITERRE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Atmo | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Planet Watchers | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | SPACE KNOW | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Rezatec | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | ASTERRA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | SATSURE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Risilience | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | AIDASH | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | LiveEO | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | SYNMAX | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | ICterra | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | OVERSTORY | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | regrow | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | vibrant planet | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | EOS data analytics | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | entelligent | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Jua | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | SKYWATCH | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | GAIT | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | URSA SPACE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | CAPE ANALYTICS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Atlas AI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | TRANIS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | GEOSPATIAL INSIGHT | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | CLIMATE AI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | ANALYSE | SATELLITE DATA | Acclym | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | xFarm Technologies | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Treefera | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Mitiga Solutions | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Climate X | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | PERSEFONI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Sylvera | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Concirrus | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Climavision | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | NCX | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Agreena | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | Pachama | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | EARTHOPTICS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | RENOSTER | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | BeZero | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | EARTH AI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | KAYRROS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | CLIMATE | JUPITER | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | Sparta | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | ChAI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | Arbol | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | Raincoat | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | Descartes Underwriting | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | kettle | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | FloodFlash | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | FLOODBASE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | PULA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | http://zesty.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">zesty.ai | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | reThought | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | INSURANCE | Delos | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | Vermeer | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | Neara | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | FocalPoint | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | unacast | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | what3words | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | swift NAVIGATION | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | next billion.ai | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | mapbox | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOCATION&MAPPING | carto | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | Prewave | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | logcomex | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | WINDWARD | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | Beacon | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | zeitview | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | SHIPPEO | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | VIZION | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | LOGISTICS | project44 | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | WORLD LABS | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | Voxel51 | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | blackshark | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | ceres | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | BIFROST | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | RAIC Labs | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | VORTEXA | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | MODERN INTELLIGENCE | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | DANTI | |
| DOWNSTREAM | PRODUCT | OTHER | unabiz | |
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | Katalyst Space Technologies | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | ALDORIA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | SPACE MACHINES COMPANY | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | clearspace today | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | Astrocscale | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | NORTHSTAR | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | KEPLER | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | LEOLABS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | SLINGSHOT AEROSPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | OKAPI | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | STARFISH SPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | PRIVATEER | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | ORBITFAB | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | True Anomaly | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | TURIONSPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | Kurs Orbital | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | DIGANTARA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | VYOMA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | HEO Robotics | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE SERVICES | RHEA SPACE ACTIVITY | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | Starpath Robotics | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | Lunar Outpost | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | Karman+ | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | Interlune | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | OFF WORLD | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | QOSMOSYS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | ASTROLAB VENTURI | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | ispace | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | ASTROBOTIC | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | Virgin Galactic | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | INTUITIVE MACHINES | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | EXPORATION & UTILIZATION | ASTRO FORGE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | STARFLIGHT DYNAMICS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | LambdaVision | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | Exobiosphere | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | Astral Materials | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | Astral Materials | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | SPACE FORGE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | SPACE TANGO | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | VARDA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | SOLAR FOODS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | CISLUNAR INDUSTRIES | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | IN-SPACE R&D / MANUFACTURING | SPACE PHARMA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Zeno Power | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Venus Aerospace | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Starcloud | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Star Catcher | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Reflect Orbital | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Antares Nuclear | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | AETHERFLUX | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | AXIOM SPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | GITAI | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | VOYAGER SPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | QUANTUM SPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | GRAVITICS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | The Exploration Company | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Inversion | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | Vast | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | REDWIRE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | OUTPOST | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | SIERRA | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | ATMOS | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | OVERVIEW ENERGY | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | RADIAN AEROSPACE | ||
| IN-SPACE ECONOMY | SPACE INFRASTRUCTURE | ELEVATION SPACE |
Current status and prospects of the job market in the space industry
As many space tech companies accelerate their space-related projects, the demand for engineers and other professionals is increasing rapidly. This section provides an overview of the current and future job situation in the space tech industry.
Current job market
① Overall job trends
- Increased demand for jobs
The number of jobs in the space technology industry is increasing year by year, with demand rising, particularly for positions related to satellite launches and space exploration. By region, there is a wide variety of jobs in the USA and Europe, where the market is large.
② 2026 Salary Trends: Shifting Compensation Amid Intensifying Talent Competition
- Rising Salary Standards
Until a few years ago, space ventures were often perceived as “inspiring but low-paying.” As of 2026, that reality has shifted. With the government’s Space Strategy Fund now in full swing, companies have moved from the “R&D” phase to “Commercialization and Mass Production.”
This transition has ignited fierce competition for talent ready to make an immediate impact. To headhunt high-class professionals from other industries—such as automotive, IT, trading houses, and finance—salary levels are showing a definitive upward trend. - The Growing Reality of Stock Options (SO)
Beyond base salary, Stock Options have become a crucial factor. Since 2024, the industry has seen a rise in successful IPOs and M&A activity among space companies.
Bolstered by strong government backing, many startups have entered a phase where going public is a realistic milestone. Consequently, many firms now offer robust stock option programs. The ability to see your personal contributions directly increase company value—and subsequently your own future assets—remains one of the most compelling draws of the venture ecosystem.
③ Job types with the majority of vacancies
- Engineering positions (rocket, satellite)
There are many opportunities in engineering jobs related to satellite development and rocket launches. Due to the increasing complexity of each project, engineers with a wealth of practical experience are required, and it is generally a difficult field for those with no industry experience to take on the challenge. Embedded software engineers are also required to have a major or experience in a similar field, such as automotive or robotics. - Data scientist and analytical engineer
These positions analyse the vast amounts of data acquired from satellites and space exploration missions, and are in increasing demand by governments and commercial companies in many countries, particularly for their ability to utilise AI and big data.
④ Regional job trends
- USA
The USA is a leader in space tech, with some 6,400 space companies (as of 2021), mainly large companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, Boeing and Northrop Grumman, generating a relatively large number of job opportunities. Engineering jobs are also increasing, particularly in California, where SpaceX is also headquartered, and in Texas, which is home to many technology companies and has historically been a leader in space exploration from the Johnson Space Center.On the other hand, reports indicate that under the Trump administration, changes to space policy and mounting pressure to slash the NASA budget led to the departure of approximately 4,000 employees—more than 20% of its total workforce—in 2025.
There are growing concerns that the ripple effects will reach NASA-affiliated contractors and the broader private sector. Some reports suggest that this has already triggered localized instability, characterized by a decrease in job openings and an “outflow” (brain drain) of engineers to other countries. - EU
Europe is also seeing an increase in job opportunities, particularly in ESA (European Space Agency) and Airbus Defence and Space. The UK (world’s second-largest space company), Germany (fourth-largest) and France (seventh-largest) are of particular interest, as are their participation in space exploration and communications satellite projects.
⑤ 2026 Recruitment Trends: What’s Happening on the Front Lines
It has been two years since the formulation of the “Space Technology Strategy” in 2024 and the subsequent rollout of the “Space Strategy Fund.” As of 2026, the recruitment landscape is seeing an unprecedented demand for professionals who can “accelerate and stabilize” business operations.
- Surge in Engineering Demand: Shifting from “One-offs” to “Mass Production”
An increasing number of companies have moved beyond the R&D phase and are transitioning to the mass production of satellites and rockets. Consequently, the value of talent with experience in production control, quality assurance (QA), and supply chain management (SCM)—cultivated in industries like automotive and electronics—is skyrocketing, even for those with no prior experience in the space sector. - The Need for “Translators”: Space Data × Terrestrial Business
The industry is hungry for Business Development (BizDev) professionals with “domain expertise” who can bridge the gap between satellite data and existing sectors like agriculture, logistics, finance, and disaster prevention. While space-specific knowledge can be acquired on the job, individuals who deeply understand the client’s pain points are highly valued as immediate assets. - Corporate Roles Driving Global Expansion
As Japanese space ventures increasingly venture into international markets, there is a surge in openings for corporate functions—such as Legal, PR, and HR—capable of negotiating in English. According to the Talisman Space-Tech Team, job postings for these roles have increased approximately 1.5x compared to 2024.
⑥ Changing job needs of space tech companies in Japan.
- Changing talent needs in each phase of the business
During the business start-up phase in space ventures, there is a high need for business positions and other positions that oversee the entire project. As the commercialisation and mass production phases progress, there is a tendency for highly specialised positions such as technical/solutions and manufacturing positions to be sought after.
The ideal candidate needs to be breakthrough and highly motivated in order to create and expand innovative businesses, and all positions tend to require people who can work on a global scale.
(Source: 令和4年度宇宙産業技術情報基盤整備研究開発事業(SERVIS プロジェクト)のうち宇宙産業人的基盤強化に資する 調査事業 事業報告書 令和5年3月 デロイト トーマツ コンサルティング合同会社)
Future prospects for the job market in the space industry
① New projects and their impact on the job market
- Increase in low earth orbit (LEO) satellite projects
Business using low earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations is accelerating worldwide, including SpaceX’s Starlink in the USA, and the demand for engineers is expected to increase further as a result. In particular, the number of engineering jobs in satellite design and system operations is expected to increase. - Expansion of space exploration missions
Private companies as well as state-affiliated organisations are actively participating in space exploration missions, such as NASA’s privately procured payload transportation services (CLPS) to the Moon. Demand is expected to continue in projects related to Mars and lunar exploration, making this a field where long-term career development is possible.
② Occupations expected to increase in the future
- Attitude and Orbit Control System (AOCS) engineers
The increase in the number of satellites creates a greater demand for attitude and orbit control system (AOCS) engineers, who are particularly needed for satellite communications and observation missions, as they provide the technical support to ensure that satellites maintain their orbits accurately and are able to carry out their missions. - Flight Dynamics Engineer
The role of flight dynamics engineers, who perform orbit calculations and predictions during satellite operations and launches, is also becoming increasingly important. The need for such specialists will increase, especially in complex missions involving multiple satellites. - Data scientist
As the amount of data acquired from satellites grows, the demand for data scientists to analyse data and develop AI-based systems will continue to increase. Data analysis for new satellite missions, earth observation and weather data will become more advanced.
③ Examples of growth segments
- Commercial space travel
In September 2024, the first ever ‘extra-vehicular activity’ in space by a private citizen was widely covered in the news by a SpaceX spacecraft. Commercial space travel led by SpaceX and Blue Origin is expected to continue to develop, and new occupations are likely to emerge, such as astronaut training, mission support and life support in the space environment. - Sustainability and space debris disposal
With the increase in satellite destruction experiments and small satellite constellations, space debris is also increasing at an accelerated rate, and the deterioration of the space usage environment is becoming an issue. As rules are developed around the world regarding the control of space debris generation in orbit and the reduction of space debris, demand for companies with debris disposal technology and satellite life extension technology is expected to increase and new jobs related to these technologies are also expected to increas.

Tips on finding a job in the space industry
1. How to find jobs
① Use of major job websites
- LinkedIn↗︎
‘LinkedIn’ is a powerful tool that allows you to connect directly with space exploration companies and recruiters through a global network. By keeping your profile up-to-date and highlighting your relevant skills and experience, you can expect to be scouted by agents and recruiters. - space-job.jp↗︎
The space industry-focused job site ‘space-job.jp’ is a valuable source of information on job vacancies at space-related companies in Japan and abroad. It is a particularly strong ally for jobseekers targeting the Japanese market. - SPACE CREW↗︎・Space-Careers↗︎
SPACE CREW and Space Careers (Europe-centric) are the best places to look for international space-related careers. They cover a wide range of positions in engineering, research and development and project management. - Japan Dev↗︎
Japan Dev is a job site dedicated to engineers working in Japan, but you can also find jobs related to space exploration. The site is particularly useful for jobseekers looking to work for foreign companies or start-ups.
② Use of agents and scouting services
- Advantages of using a recruitment agent
Recruitment agents with expertise in the space exploration industry are more likely to be able to introduce you to private jobs, and there are many scouting opportunities available through these agents. They can also help you brush up your resume and prepare for interviews, so you can proceed with confidence even if this is your first job change.


- Use of the scout function
It is important to enable the scout function on LinkedIn and other job sites and make your profile attractive. In particular, detail your technical skills and experience in space exploration projects to catch the attention of company recruiters.
2. Interview preparation specific to the space industry.
①The “Three Hurdles”: Common Interview Questions in the Space Industry
Interviews at space ventures often test your “readiness” in ways that differ from typical IT firms. Here are three common questions and the best strategies for answering them.
Q1. “Why a private venture instead of a public agency like NASA or JAXA?”
- The Intent: They are checking if you have a business mindset focused on “speed and monetization” rather than the “stability and research” focus of public institutions.
- Answer Tip: Emphasize a business perspective: “I want to go beyond academic research to implement technology in society and convert it into customer value at the fastest possible pace.”
Q2. “This project has a high probability of failure. How will you handle that?”
- The Intent: In the space business, setbacks (like launch failures) are a reality. The interviewer is testing your resilience.
- Answer Tip: Avoid “pure grit” or emotional arguments. Instead, demonstrate logical risk management: “I anticipate risks to a specific degree, prepare ‘Plan B’ scenarios, and focus on how to extract data from failures to optimize the next attempt.”
Q3. “How specifically will your skills solve our current challenges?”
- The Intent: This is meant to filter out candidates who are only driven by “admiration” for the stars.
- Answer Tip: Passion for space is a given. Go further by discussing your tangible contribution: “I will inject the mass-production expertise I gained in the automotive industry into your satellite production phase to reduce costs by X%.”
② Examples of frequently asked questions
- Technical questions
The space industry requires an in-depth understanding of the technical aspects of the industry, so many of the interview questions relate to technical specialisms. Technical interview questions are often related to your personal experience (CV) and you should be able to talk about them in depth by reviewing your own background rather than preparing for a pattern. From the stage of preparing your application, you should be looking ahead to the interview, reviewing your basic knowledge of your field of expertise and preparing to showcase your practical experience. - Questions on project experience
There are always questions about past projects. You should be able to give specific details about the scale of the projects you were involved in, the technical challenges and your role in the team. Highlight how you solved problems and contributed to the success of the project to demonstrate your practical skills. - Questions about company and national culture
The fit with the culture of the company and the country is also a key factor to be checked. This is to minimise any gaps in the working environment and working style that you may experience after joining the company. For example, if you are moving from the US to Japan, you may be asked about the unique Japanese business style and salary gap.
③ Key points in the interview.
- Emphasise problem-solving skills
In the field of space exploration, the ability to deal with unknown challenges is of great importance. Therefore, the key to success in an interview is to demonstrate your ‘problem-solving’ and ‘innovation’ skills. It is a good idea to prepare specific episodes of how you solved technical problems and troubles you actually experienced. - Teamwork and communication skills
Cooperation with multinational and multidisciplinary teams is essential in the space industry. In interviews, demonstrate your leadership and communication skills by talking about your role in teams on previous projects and specific examples of collaboration with other departments.
Support for career change from Talisman Corporation
For a successful career change in the space industry, professional support is recommended. Talisman can offer comprehensive support tailored to the needs of jobseekers. Below are some of our key support offerings
1. CV review and brushing up of applications
- Checking the aspirations and requirements of job seekers
First, we interview candidates in detail about their specific career goals, work location and position preferences. By confirming the desired technical field and career path, we identify the most suitable company and position for the candidate, rather than simply a vague motive such as ‘I want to be involved in space development’ or ‘I want to work in Japan’ for job seekers from overseas. This process enables a high degree of matching accuracy that cannot be achieved by direct application.
2. Interview preparation and follow-up support
- Anxiety relief and interview preparation
Before going to the interview, job seekers are encouraged to share any concerns or questions they may have and are supported to feel confident during the interview. Advice is also given on how to respond to specific questions and how to prepare for technical questions specific to the space industry. We also provide prompt post-interview feedback to identify additional information and areas for improvement to help you take the next step. - Dealing with differences between Japanese and foreign interviews.
Particularly for candidates from overseas, we provide detailed explanations of the differences in Japanese interview styles and corporate culture. We also support the interview process for each position and adjust the interview schedule according to the company’s wishes. As a liaison with the company, we ensure smooth coordination until an offer is made and that the job seeker can proceed through the process without anxiety.
3. Coordination for multiple selection processes
- Scheduling and information sharing
When a job seeker is interviewing with several companies, the agent shares their schedules and the progress of the selection process with them, and coordinates the interviews so that they can proceed at the optimum time. Support to help you efficiently complete multiple selections and make a decision at the best possible time, without feeling rushed, is one of the major advantages of using an agent.

| Canditdates | Position before the change of job | Post-change position. | Points leading to offers |
|---|---|---|---|
| French, 45 years old. | Engaged in embedded software development in C in accordance with the European Committee for Space Standards (ECSS) for a space development organisation. | Senior Flight Software Engineer involved in software design for attitude control | Affinity of experience and skills from previous jobs, including development languages, team development experience and communication skills were valued |
| American, 35 years old | Aircraft-related embedded senior software engineer | Embedded software engineers (computer vision/flight software for robotics) | 5+ years’ experience as a part-integrated engineer, Linux embedded programming experience in C/C++ and shell scripting matches the recruitment requirements |
| Indian, 29 years old | Satellite control operations engineer for a communications satellite company | Satellite operations engineer for satellite business enterprise | Highly commended for holding an aerospace engineering-related degree, and for the consistency of work and experience with previous jobs |
🌟 Interested in working in Japan’s space tech industry?
・Search jobs on our Job Board
・Talk to Talisman about your new job
・Follow us on Linkedin to stay updated!
・Subscribe to the Newsletter